You will benefit from:
- Access to ApconiX scientists who will tailor our service specifically to your needs and better advise you on your next steps
- High quality ion channel profiling matched to your design-make-test cycle
- An average turnaround time for hERG data of less than 4 days following receipt of customer compounds

Our services include:
- Ion channel screening for hERG, cardiac and neuro liabilities, and all elements of the CiPA paradigm including the ion channel panel (hERG, hNav1.5 peak and late current, hKvLQT1, hKv4.3, hCaV1.2, hKir2.1), in silico action potential modelling, and investigation in hiPSC-cardiomyocytes
- Bespoke assay and cell line development
- Expertly performed direct functional electrophysiology measurements with fewer artefacts than ligand-binding or fluorescence assays
- Testing by manual patch-clamp or on the latest generation automated electrophysiology platforms (QPatch II and Patchliner) with the capacity for large numbers of compounds

Investigating Cardiac Liability
By working with ApconiX you will benefit from our combined expertise in ion channel electrophysiology and project toxicology to move molecules away from this liability through informed choices in molecule design.
Our electrophysiology experts will rapidly generate high-quality hERG screening data for your drug discovery programme with an average turnaround time for hERG data of 4 days.
Here’s which ion channels are routinley screened in the pharma industry (Authier et al., 2017):
NaV1.5 is cardiac sodium channel, CaV1.2 is cardiac “L-type” calcium channel, kvLQT1 is cardiac lks current
Refine your decision making with a deeper understanding of the potential for effects on cardiac safety to deliver an optimal and de-risked clinical candidate. ApconiX routinely offer sodium and calcium channel assays for a more comprehensive assessment of cardiac liability. On a case-by-case basis we can also deploy other cardiac ion channel assays to suit your needs including cardiac ‘T-type’ calcium channels and Kv1.5 as well as more advanced models of cardiac safety such as Purkinje fibre, cardiac contractility and Langendorf models.
It is a regulatory requirement that an assessment of hERG inhibition should be made by manual patch-clamp to Good Laboratory Practise (GLP) standards. GLP-hERG is provided through our expert partners.
Given over 500 years of combined expertise in drug discovery and safety, ApconiX is uniquely positioned to work with your project team to
interpret your data in the context of your drug discovery program.
Comprehensive in vitro Proarrhythmia Assay (CiPA)
The regulations regarding the testing of new drugs for cardiac safety are changing. ApconiX can help you understand how these new regulations will affect you and guide you through the testing process. We are working with a number of stakeholders to create this new regulatory framework called CiPA (Comprehensive in vitro Proarrhythmia Assay). The new paradigm will include the testing of a wider panel of ion channels, in silico modelling of ion channel data and measurements using human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.
ApconiX offers two critical experimental components of the CiPA assay package:
- Ion channel testing of compounds against these cardiac ion channels: hERG, hNaV1.5 (peak current), hNaV1.5 (late current), hCaV1.2, hKir2.1, hKv4.3 (to current) and hKvLQT1/mink (Iks current)
- Action potential measurement and proarrhythmia detection in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
We continue to work with expert partners to provide in silico modelling and AP prediction.
We are always here to give you the advice you need to take an informed next step and we will support you to make the right decision.
ApconiX offers two critical experimental components of the CiPA assay package:
- Ion channel testing of compounds against these cardiac ion channels: hERG, hNaV1.5 (peak current), hNaV1.5 (late current), hCaV1.2, hKir2.1, hKv4.3 (to current) and hKvLQT1/mink (Iks current)
- Action potential measurement and proarrhythmia detection in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
We continue to work with expert partners to provide in silico modelling and AP prediction.
We are always here to give you the advice you need to take an informed next step and we will support you to make the right decision.
Investigation of potential cardiotoxicity in hiPSC-cardiomyocytes using the Maestro Pro MEA assay system (Axion Biosystems).
The microelectrode array (MEA) in vitro cardiotoxicity assay measures the effect of compounds on action potential, field potential (FP), propagation and contractility. This data can be used to build a picture of compound cardiac liability before costly in vivo work.
Compound effect on action potential duration (APD, Figure 1a ) and changes in morphology are identified using local extracellular action potential assays (LEAP). This is a non-invasive tool allowing the visualisation of arrhythmias for example early after depolarisations (EAD’s, Figure 1b).
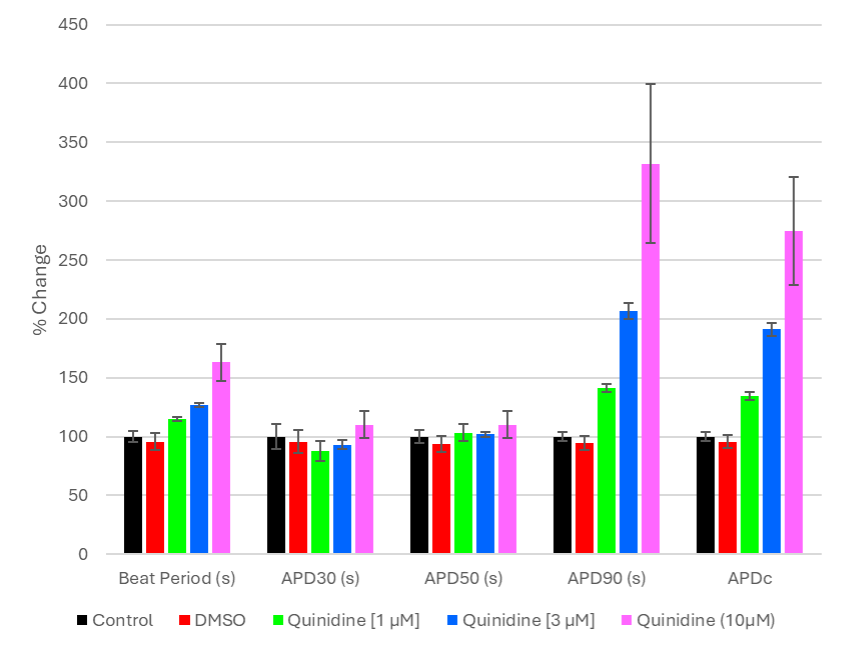
Figure 1a. LEAP metrics measured under normal conditions and in the presence of increasing concentrations of Quinidine.
Quinidine addition (Na+ and K+ channel blocker) results in the prolongation of repolarisation giving rise to an increase in beat period and action potential duration.
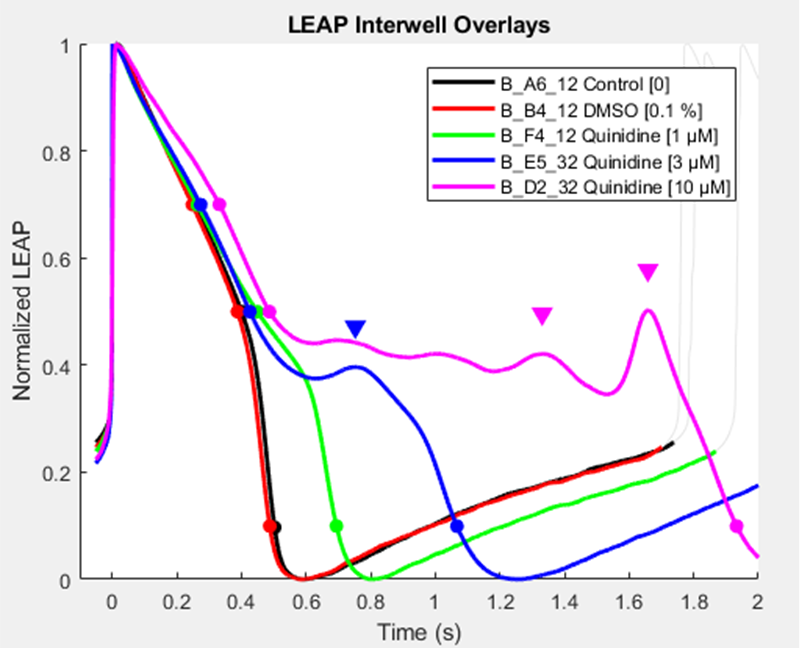
Figure 1b. LEAP measurements observed under normal conditions and in the presence of Quinidine
Quinidine at low dose causes a prolongation of repolarization, as the dose increases EAD’s are observed.
Flexibility and customer focus
Our clients may have known impurities in their test compound and need to understand the effect these may have in our assays. We are happy to investigate the effect of impurities in your preparations.
We also realise not all compounds are soluble in standard organic solvents, e.g. DMSO. Our clients are often looking for ways to increase the solubility of their compounds with a variety of organic and aqueous solvents. We are happy to try a number of solvents which have been validated in our assays.









